HyperBMC
BMC-Centric, Software-Defined Platform Management for Datacenter Efficiency, Security, and Low Entropy
HyperBMC
| 中文 | English |
A software-defined platform management solution powered by BMC as the execution engine, enabling energy-efficient, high-performance, and secure operations for computing infrastructure.
Overview
HyperBMC represents a transformative approach to computing infrastructure management that positions the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) as an intelligence engine. Our solution redefines how modern computing power centers achieve security, efficiency, and intelligent management at scale.
The prefix “Hyper” embodies our ambition to transcend conventional boundaries — beyond traditional management paradigms, beyond standard security practices, and beyond existing efficiency metrics. With HyperBMC, we are building a next-generation management plane that delivers unprecedented levels of automation, trustworthiness, and sustainability in computing power center operations.
What is BMC?
The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) is a dedicated microcontroller embedded in server motherboards that provides an independent management subsystem. Operating separately from the main CPU and operating system, it enables Out-of-Band (OOB) control and monitoring — ensuring that administrators can manage servers even when they are powered off or unresponsive.
HyperBMC Vision: Beyond Tradition
HyperBMC redefines the boundaries of platform management by extending the capabilities of traditional BMCs into a software-defined intelligent control layer that spans both physical and virtual infrastructure.
Software-Defined Platform Management
HyperBMC introduces a software-defined control concept to achieve unified management of the computing power center ecosystem—encompassing hardware, firmware, virtualization, and the application layer.
Zero-Trust Security
HyperBMC establishes a new foundation for secure computing through lightweight, dynamic permission control and authenticated, encrypted communication channels, enabling true zero-trust management.
Efficiency and Low-Carbon Operations
Leveraging thermal elasticity–aware provisioning and carbon-efficient resource allocation algorithms, HyperBMC optimizes not only individual server performance but also the collective energy efficiency of computing power center operations.
Beyond Current Architectures
HyperBMC transforms the BMC from a mere management controller into a coordinating intelligence that bridges hardware, virtualization, and cloud-native environments — extending traditional physical infrastructure management into the virtual infrastructure domain.
With HyperBMC, we are not just managing servers — we are defining the future of autonomous, secure, and sustainable computing power center operations.
Publications
[1] Zhang D, Xia H J, Wang X T, et al. Software-defined platform management for data center: Security, low entropy, and efficiency[J]. Cybersecurity, 2025, (Accepted).
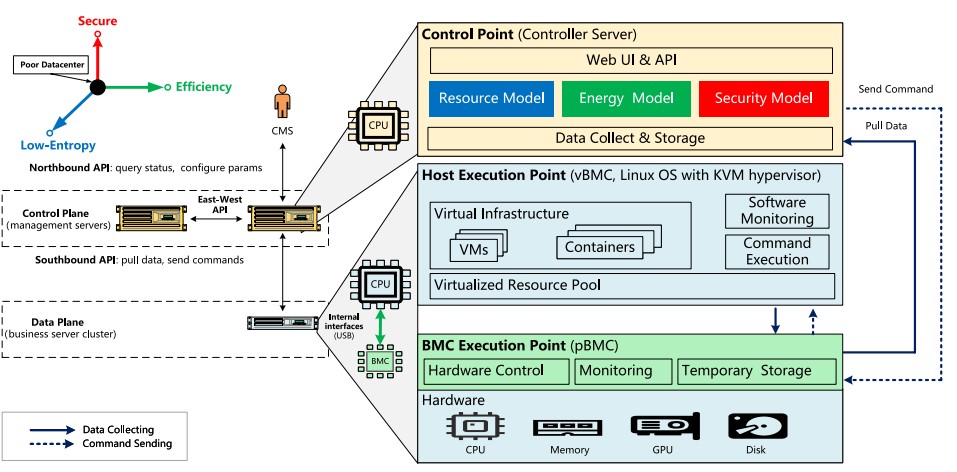
To solve rigid architecture, poor security and high scheduling entropy in traditional data center management, this paper proposes a software-defined platform management architecture. It decouples management from hardware, integrates zero-trust security, entropy optimization and architecture design. Accepted by Cybersecurity, the architecture provides new ideas for next-gen data center management.
@article{zhang2025sdpm,
author = {Da Zhang and Haojun Xia and Xiaotong Wang and Bibo Tu},
title = {Software-Defined Platform Management for Data Center: Security, Low Entropy, and Efficiency},
journal = {Cybersecurity},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.1186/s42400-025-00410-4}
}
[2] Zhang D, Xia H J, Wang X T, et al. Thermal elasticity-aware host resource provision for carbon efficiency on virtualized servers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2025, 74(11): 3682-3695.
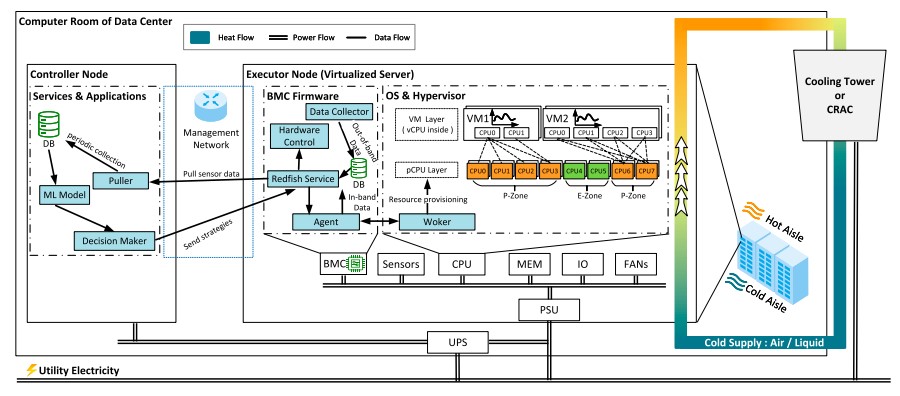
Maintaining a balance between computing resource supply and cooling capacity is crucial for enhancing server energy efficiency and stability. This paper defines the state in which power varies with load while temperature remains stable as “Thermal Resilience.” Accordingly, we propose a thermal-resilience-aware host resource provisioning method. This approach utilizes an AI model to identify the active and inactive states of thermal resilience, enabling timely adjustments to cooling capacity or resource supply to maintain resilience. The open-source code and datasets are available at: https://github.com/arealuser/bmcdata
@article{zhang2025thermal,
author = {Da Zhang and Haojun Xia and Xiaotong Wang and Yanchang Feng and Bibo Tu},
title = {Thermal Elasticity-Aware Host Resource Provision for Carbon Efficiency on Virtualized Servers},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Computers},
year = {2025},
volume = {74},
number = {11},
pages = {3682-3695}
}
[3] Liu H W, Xia H J, Tu B, et al. Research on lightweight dynamic permission control mechanism for baseboard management controller[J]. Journal of Information Security, 2022.
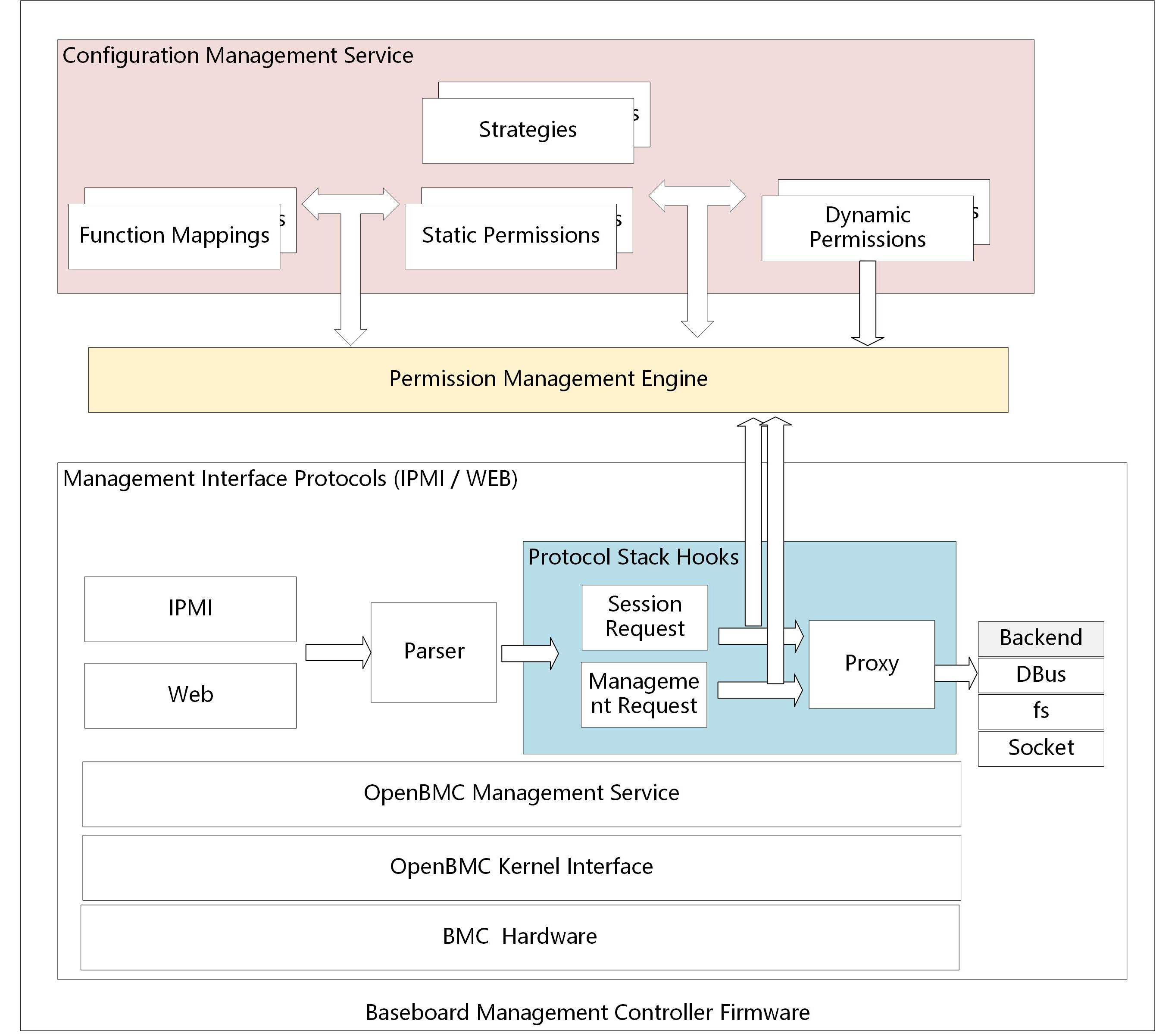
Aiming at the security risks of excessive permissions and abuse in BMCs, this paper proposes a lightweight dynamic permission control framework for resource-constrained BMCs. Its core lies in unifying cross-protocol permissions into fine-grained descriptors, implementing real-time permission management and auditing via a dynamic engine, and adopting lightweight mechanisms to reduce overhead. Experiments show the scheme ensures security with minimal performance impact, suitable for embedded BMC deployment.
@article{liu2022bmcen,
author = {Hongwei Liu and Haojun Xia and Bibo Tu and Xiaotong Wang},
title = {Research on Lightweight Dynamic Authorization Mechanism for BMC System},
journal = {Journal of Cyber Security},
year = {2024},
doi = {10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2024.02.10}
}
[4] Liu H W, Xia H J, Tu B, et al. A secure and efficient USB-based in-band communication interface between host and BMC[C]//IEEE International Conference on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications (ISPA). IEEE, 2022.
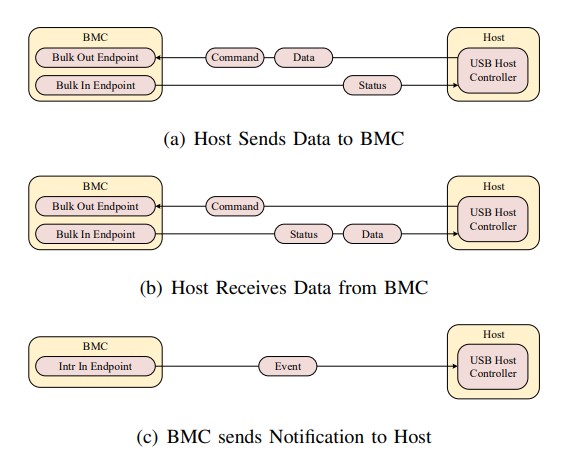
To address compatibility, security and efficiency issues of existing host-BMC communication interfaces, this paper proposes a USB-based in-band communication scheme. It customizes USB protocols for higher transmission rate, introduces end-to-end encryption and two-way authentication for security, and supports mainstream server architectures without extra hardware.
@inproceedings{liu2022usb,
author = {Hongwei Liu and Haojun Xia and Bibo Tu and Da Zhang and Xiaotong Wang},
title = {A Secure and Efficient USB-based In-band Communication Interface between Host and BMC},
booktitle = {IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications (ISPA)},
year = {2022}
}
[5] Liu H W, Xia H J, Tu B. Secure and efficient BMC-based centralized management method for large-scale data centers[C]//2022 IEEE 24th International Conference on High Performance Computing & Communications (HPCC). IEEE, 2022: 1328-1335.
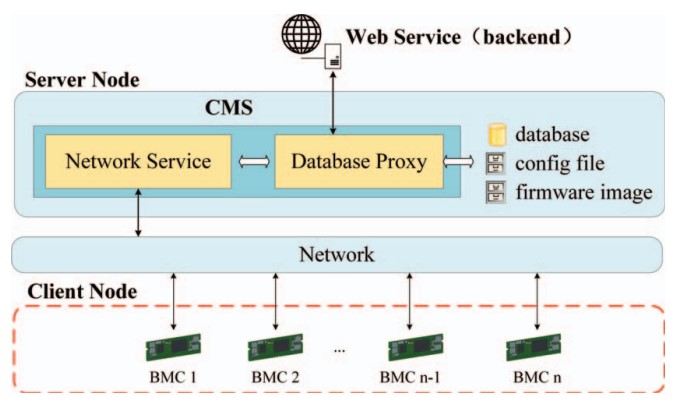
Aiming at the inefficiency and high O&M costs of traditional distributed management in large-scale data centers, this paper proposes a secure and efficient BMC-based centralized management method. It achieves unified BMC access, secure data transmission via encrypted links, and efficient management via lightweight compression and batch processing.
@inproceedings{liu2022secure,
title={Secure and efficient BMC-based centralized management method for large-scale data centers},
author={Liu, Hongwei and Xia, Haojun and Tu, Bibo},
booktitle={2022 IEEE 24th Int Conf on High Performance Computing \& Communications (HPCC)},
pages={1328--1335},
year={2022},
organization={IEEE}
}
[6] Zhang D, Xia H J, Wang X T, et al. Interference monitoring for colocated workloads in low-entropy computing systems[C]//28th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD 2025). 2025.
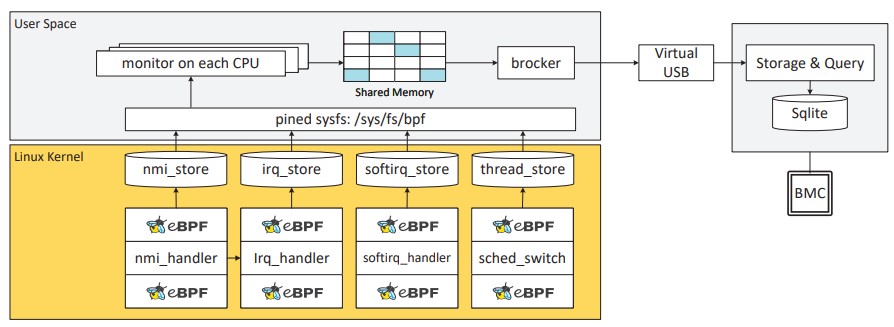
Workload colocation in low-entropy systems causes resource interference and degraded QoS. This paper proposes an interference monitoring method, using lightweight agents to collect key indicators, machine learning for interference identification, and adaptive strategies to balance accuracy and overhead.
@inproceedings{zhang2025interference,
author = {Da Zhang and Haojun Xia and Xiaotong Wang and Yanchang Feng and Bibo Tu},
title = {Interference Monitoring for Colocated Workloads in Low-Entropy Computing Systems},
booktitle = {28th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD 2025)},
year = {2025}
}